Introduction of Vacuum Disk Filter
As an efficient solid-liquid separation device, vacuum disc filter has a wide range of applications in mining, chemical industry, environmental protection and many other fields. It mainly relies on the principle of negative vacuum pressure to carry out the work, under the action of negative vacuum pressure, the liquid in the suspension can pass through the filtration medium, while the solid particles will be effectively retained by the filtration medium, and then accumulate on the surface of the filtration medium to form a cake, so as to achieve the purpose of solid-liquid separation.
Compared with other types of filtration equipment, the advantages of vacuum disk filter are more significant, with the ability of continuous operation, and can be uninterrupted solid-liquid separation operation, which greatly improves the production efficiency. High filtration efficiency, can achieve efficient solid-liquid separation effect in a relatively short period of time, and the degree of automation is also at a high level, which can effectively reduce manual intervention and lower labor costs. For this reason, vacuum disk filters occupy a key position in large-scale industrial production scenarios.

Working Principle
Vacuum disk filter mainly relies on vacuum negative pressure to realize solid-liquid separation, and its workflow is as follows:

Feeding: The suspension to be filtered, transported to the filter disk below or around the filter disk, so that the disk is submerged in it;
Vacuum adsorption: The inside of the disk is connected to the vacuum system through the pipeline, and after the vacuum is turned on, a pressure difference will be generated inside and outside of the disk. Under the action of pressure difference, the liquid in the suspension will enter the liquid collection channel inside the filter disk through the filter cloth, and the solid particles will be retained by the filter cloth, forming a cake on the surface of the filter disk;
Cake dewatering: In the process of filtration, the cake is constantly thickening, and the negative pressure of the vacuum continues to work to further extract the residual water in the cake and reduce the moisture content;
Unloading: The cake will be unloaded in the discharge area after reaching a certain thickness and dryness, at this time, the vacuum system is closed and the water will be blown back or scraped off by the compressed air or scraper. Through compressed air or scraping with a scraper, the cake is stripped from the surface of the filter cloth and collected;
Filter cloth regeneration: After unloading, part of the filter will be rinsed with water or compressed air blowing the filter cloth to remove residual fine particles, to restore the filter performance of the filter cloth, and to be ready for the next filtration.
The whole process rotates continuously with the help of the filter disk to realize the cyclic operation of each stage and achieve the effect of continuous solid-liquid separation.
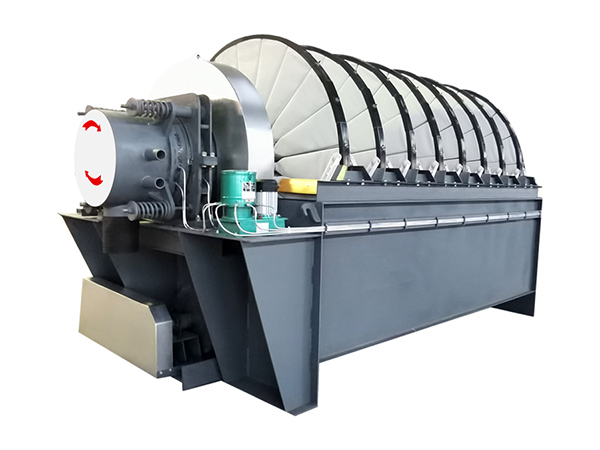
Structure
Vacuum disk filter is mainly composed of the following core components
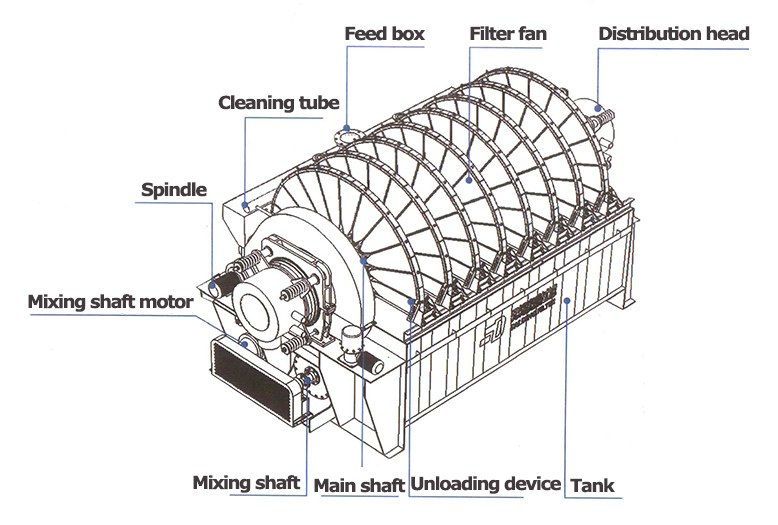
Tank body
It is a container for filtering suspension, and the filter disk is partially submerged in the slurry in the tank, and a stirring device is standing at the bottom of the tank body to prevent the slurry from settling.
Vacuum system
It covers vacuum pump, vacuum tank, pipeline and valve, which can provide stable negative pressure and discharge the filtrate.
Discharging device
It contains squeegees and compressed air blowing system.
Transmission system
It consists of electric motor, gear reducer, gears or chains. 4, transmission system: composed of motor, reducer, gear or chain, drive the filter disk to rotate at a speed of 0.5 to 3r/min to realize the switching of various working stages
Filter disk
The core filtration unit, generally composed of 6-20 fan-shaped filters put together into a circle, the surface is covered with filter cloth, and the interior is equipped with a radial or circular liquid collection channel to collect the filtrate through the filter cloth
Control system
The core of the PLC, with the vacuum, liquid level and other sensors, can automatically control the Control system: PLC as the core, with vacuum, liquid level and other sensors, it can automatically control the feeding volume, vacuum, speed and other parameters, and part of the equipment is equipped with touch screen to realize man-machine interaction.
What are the advantages of vacuum disk filters compared with plate and frame filters and belt filters:
| Comparing dimensions | vacuum disk filter | Plate and frame filter | Belt filter |
| Operating mode | Continuous operation, completing stages such as feeding, filtering, and discharging through the rotation and circulation of the filter disc | Intermittent operation involves several steps, including framing, feeding, filtering, unframing, and cleaning. Each stage requires machine downtime for switching | Continuous operation, achieving continuous feeding, filtering, dewatering, and unloading through the continuous running of the filter belt |
| Filtration efficiency | High, with a processing capacity per unit area of 0.5~3m³/(m²・h), and fast filter cake formation driven by vacuum negative pressure | Medium, with filtration speed gradually decreasing as the filter cake thickens, suitable for small batches and materials with high solid content | Moderately high, with processing capacity influenced by the speed and width of the filter belt, it is generally suitable for medium and low concentration slurry |
| Water content of filter cake | Relatively low, ranging from 15% to 30%, the moisture content can be further reduced through the combination of vacuum negative pressure and back blowing | Low to medium, ranging from 10% to 30%. High-pressure pressing can significantly reduce the moisture content, but additional pressure equipment is required | Medium, 20% to 40%, mainly dehydrated through gravity filtration and low-pressure pressing, with a moisture content slightly higher than that of vacuum disc and plate and frame filters |
| Degree of automation | It is relatively advanced, and parameters such as vacuum degree, rotational speed, and feed rate can be controlled through PLC. Unloading and filter cloth regeneration can be automatically completed | The cost is relatively low, and the processes such as frame installation and removal rely heavily on manual operations. Some fully automatic models have higher costs | It is relatively high, and can automatically control the filter belt speed, flushing water volume, etc., with no manual intervention required for unloading |
| Adaptability | Suitable for slurries with concentrations ranging from 5% to 60% and particles ranging from 1 to 200μm, such as mining concentrates and chemical slurries | Suitable for high-concentration and high-viscosity materials such as dyes and food waste, with strong adaptability to particle size (able to retain fine particles) | It is suitable for slurry with medium to low concentration (3% to 30%) and coarser particles, such as municipal sludge and mine tailings. However, handling viscous materials poses a significant challenge |
| Cover an area | Relatively small, with a more compact layout for the same processing capacity | It is relatively large, requiring space for frame installation and removal operations. The overall volume of the equipment is quite bulky | It is relatively large, and due to the need to arrange filter belts, feeding devices, press rolls, flushing systems, etc., it is usually quite long in length |
| Equipment cost | It is relatively high, requiring complex components such as a vacuum system and a transmission system | Low in cost and simple in structure, it primarily consists of a filter plate, a filter frame, and a clamping device | The equipment is relatively complex, requiring components such as filter belts, drive systems, pressing devices, and flushing systems, making it more complex than the plate and frame filter press |
| Operating cost | Moderate. Vacuum pumps have higher energy consumption, but lower labor costs | The cost is relatively high, the labor operation cost is high, and the filter cloth wears out quickly (requiring frequent disassembly) | Moderate, with high maintenance costs for the filter belt, and energy consumption mainly coming from the drive motor and flushing water pump |
| Applicable scenarios | Large-scale industrial production, such as mining dewatering, environmental sludge treatment, and continuous filtration in the chemical industry | Small batch and intermittent production, such as laboratory small-scale experiments, fine chemicals, and high-purity filtration in food and pharmaceutical industries | Medium-to-large-scale continuous production, such as municipal sludge dewatering, mine tailings treatment, and agricultural wastewater treatment |
| Discharge method | Automatic unloading, utilizing a scraper in conjunction with compressed air back-blowing, to strip the filter cake from the surface of the filter disc | Manual or semi-automatic unloading requires dismantling the filter frame to clean the filter cake, resulting in high labor intensity | Automatic unloading, where the filter cake naturally falls off when the filter belt reaches the end, or is assisted by a scraper for stripping |
| Difficulty in replacing filter cloth | It is relatively complex, requiring disassembly of the filter disc assembly to replace the filter cloth, which takes a long time | It is relatively simple; just open the filter frame to replace the filter cloth. However, frequent replacement will affect efficiency | Itisrelativelysimple,withacircularcontinuousstructureofthefilterbelt,whichcanbereplacedonlineorquicklyreplacedaftershutdown |
Vacuum Disc Filter Manufacturer
As an efficient solid-liquid separator, the Vacuum Disc Filter achieves continuous operation by virtue of the vacuum-negative-pressure driving principle. With its compact design and outstanding level of automation, it plays a key role in a wide range of industries, especially in the dewatering of large-scale, high-concentration slurries.
Hot Tags:










